

Cluster sampling is defined as a sampling method where the researcher creates multiple clusters of people from a population where they are indicative of homogeneous characteristics and have an equal chance of being a part of the sample.
Consider a scenario where a data organization is looking to survey the performance of smartphones across Germany. They can divide the entire country’s population into cities (clusters), select further towns with the highest population, and filter those using mobile devices.
Content Index hideCluster sampling is a probability sampling technique where researchers divide the population into multiple groups (clusters) for research. So, researchers then select random groups with a simple random or systematic random sampling technique for data collection and unit of analysis.
Example: A researcher wants to conduct a study to judge the performance of sophomores in business education across the U.S. It is impossible to conduct a research study that involves a student in every university. Instead, cluster sampling allows the researcher to club the universities from each city into one cluster. These clusters then define the sophomore student population in the U.S. Next, either using simple random sampling or systematic random sampling and randomly picking clusters for the research study. Subsequently, by using simple or systematic sampling, the sophomore’s from each of these selected clusters can be chosen on whom to conduct the research study.
In this sampling technique, researchers analyze a sample that consists of multiple sample parameters such as demographics, habits, background – or any other population attribute, which may be the focus of conducted research. This method is usually conducted when groups that are similar yet internally diverse form a statistical population. Instead of selecting the entire population, cluster sampling allows the researchers to collect data by bifurcating the data into small, more productive groups.
There are two ways to classify this sampling technique. The first way is based on the number of stages followed to obtain the cluster sample, and the second way is the representation of the groups in the entire cluster analysis. In most cases, sampling by clusters happens over multiple stages. A stage is considered to be the step taken to get to the desired sample. We can divide this technique into single-stage, two-stage, and multiple stages.
As the name suggests, sampling is done just once. An example of single-stage cluster sampling – An NGO wants to create a sample of girls across five neighboring towns to provide education. Using single-stage sampling, the NGO randomly selects towns (clusters) to form a sample and extend help to the girls deprived of education in those towns.
Here, instead of selecting all the elements of a cluster, only a handful of members are chosen from each group by implementing systematic or simple random sampling. An example of two-stage cluster sampling – A business owner wants to explore the performance of his/her plants that are spread across various parts of the U.S. The owner creates clusters of plants. So, he/she then selects random samples from these clusters to conduct research.
Multiple-stage cluster sampling takes a step or a few steps further than two-stage sampling.
For conducting effective research across multiple geographies, one needs to form complicated clusters that can be achieved only using the multiple-stage sampling technique. An example of Multiple-stage sampling by clusters – An organization intends to survey to analyze the performance of smartphones across Germany. They can divide the entire country’s population into cities (clusters) and select cities with the highest population, and also filter those using mobile devices.
LEARN ABOUT: Survey Sampling
Here are the steps to perform cluster sampling:
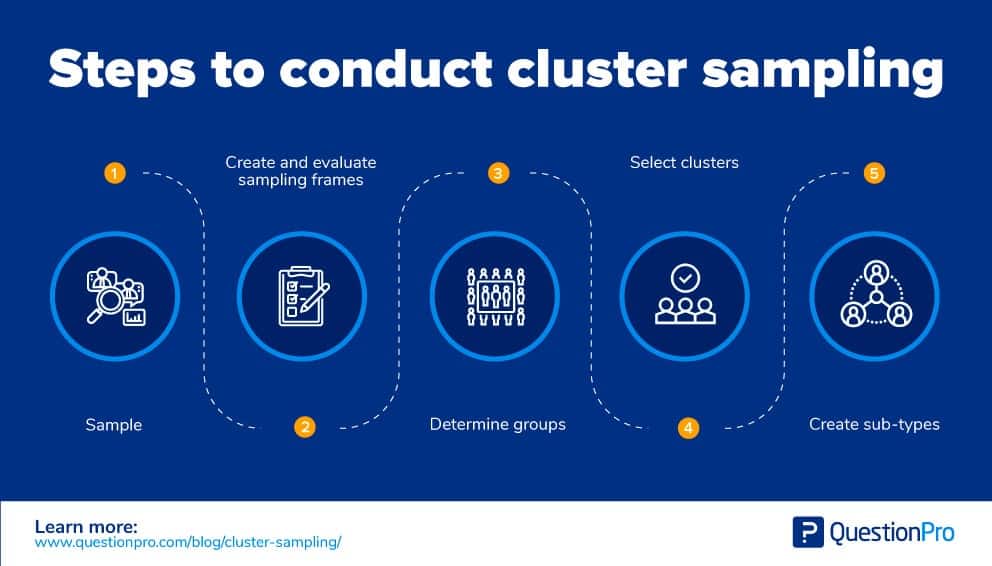
This sampling technique is used in an area or geographical cluster sampling for market research. A broad geographic location can be expensive to survey compared to surveys sent to clusters divided based on region. The sample numbers must be increased to achieve accurate results, but the cost savings make this process of rising clusters attainable.
The technique is widely used in statistics where the researcher can’t collect data from the entire population. So, it is the most economical and practical solution for research statisticians. Take the example of a researcher looking to understand smartphone usage in Germany. In this case, the cities of Germany will form clusters. This sampling method is also used in wars and natural calamities to draw inferences about a population, where collecting data from every individual residing is impossible.
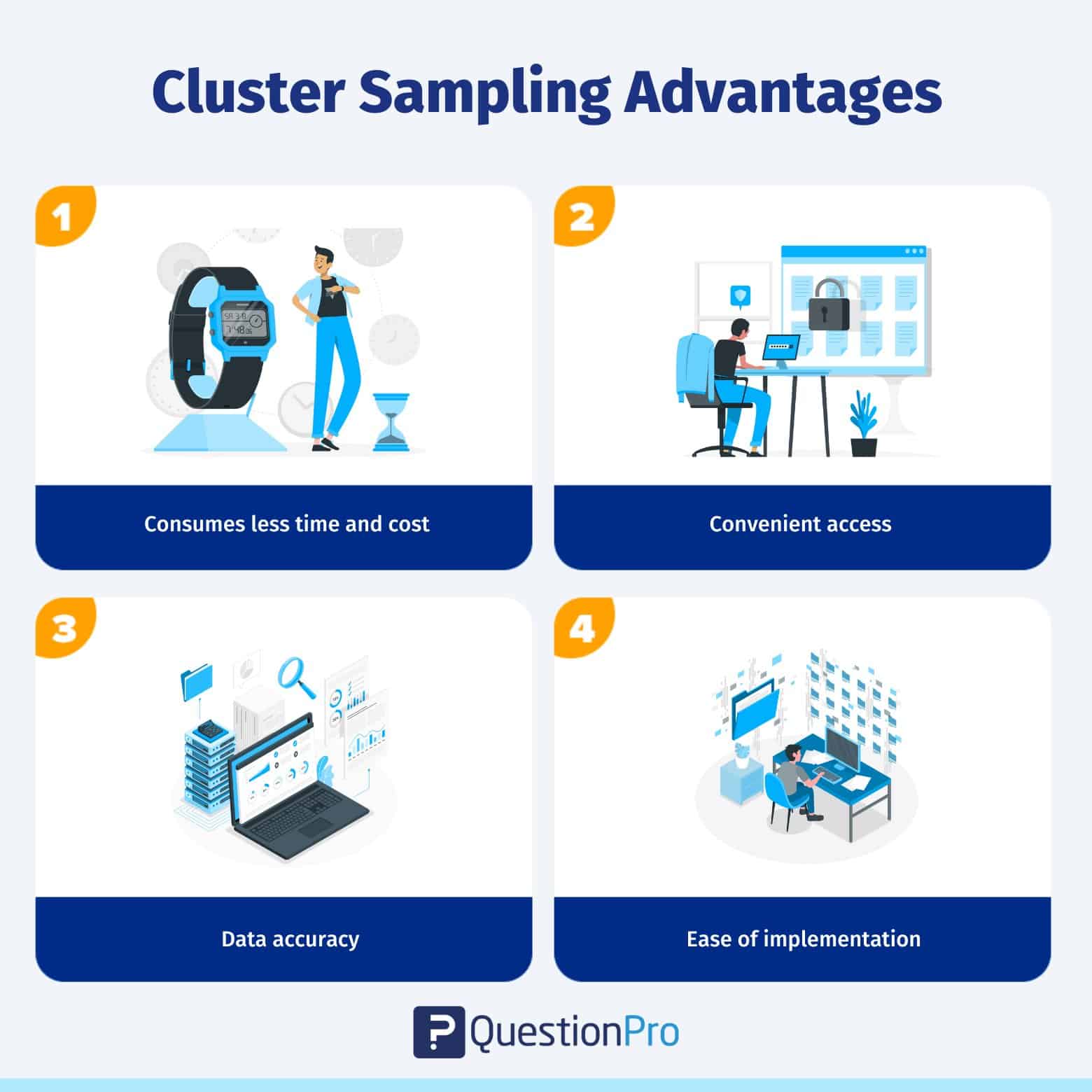
There are multiple advantages to using cluster sampling. Here they are:
In comparison to simple random sampling, this technique can be useful in deciding the characteristics of a group, such as population, and researchers can implement it without having a sampling frame for all the elements of the entire population.
Since cluster sampling and stratified random sampling are pretty similar, there could be issues with understanding their finer nuances. So let’s talk about the significant differences between cluster sampling and stratified sampling:
| Cluster Sampling | Stratified Sampling |
|---|---|
| Elements of a population are randomly selected to be a part of groups (clusters). | The researcher divides the entire population into even segments (strata). |
| Members from randomly selected clusters are a part of this sample. | Researchers consider individual components of the strata randomly to be a part of sampling units. |
| Researchers maintain homogeneity between clusters. | Researchers maintain homogeneity within the strata. |
| Researchers divide the clusters naturally. | The researchers or statisticians primarily decide the strata division. |
| The key objective is to minimize the cost involved and enhance competence. | The key objective is to conduct accurate sampling, along with a properly represented population. |
With QuestionPro, you can implement cluster sampling by dividing the target population into clusters. You can also select a random sample of these clusters to survey.
QuestionPro’s robust suite of research tools provides you with all you need to derive cluster sampling. So choose from over 22 million+ mobile-ready respondents to conduct ongoing market research studies for your research.